Cheatsheet
- Primitives
- Interface
- Glossary
Here you can find all functional building blocks at a glance!
| Primitive | Type | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
 | SD |
| Population, water level, energy content |
| SD |
| Birth rate, water inflow, energy consumption | |
 | Common |
| Census data, district data, infrastructure |
| Common |
| — | |
| Common |
| — | |
| Common |
| — | |
 | ABM |
| At home, at work, in quarantine |
| ABM |
| Healthy → infected, undecided → convinced, moving to another city | |
 | ABM |
| Get vaccinated, find the nearest bike station, influence other agents |
 | ABM |
| Car in traffic, consumer in a market model, machine in a factory |
 | ABM |
| Residents in a city, vehicles on a road, trees in a neighborhood |
Here you can find all interface components at a glance!
| Interface | Component | Functions |
|---|---|---|
 | Navibar |
|
 | My Models |
|
 | Sidebar |
|
 | Model Settings |
|
 | Clone Model |
|
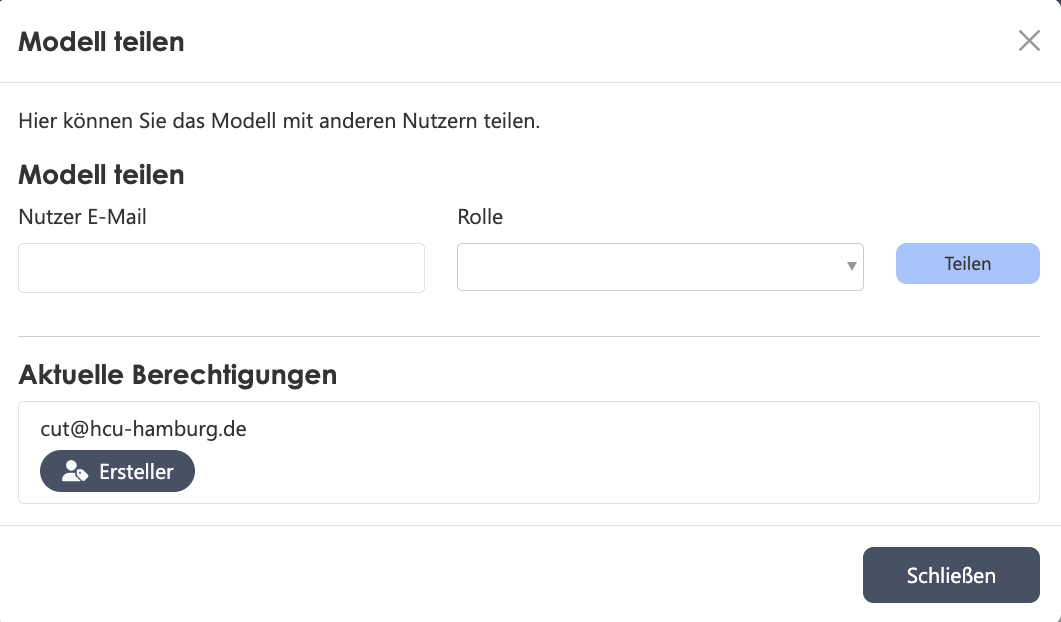 | Share Model |
|
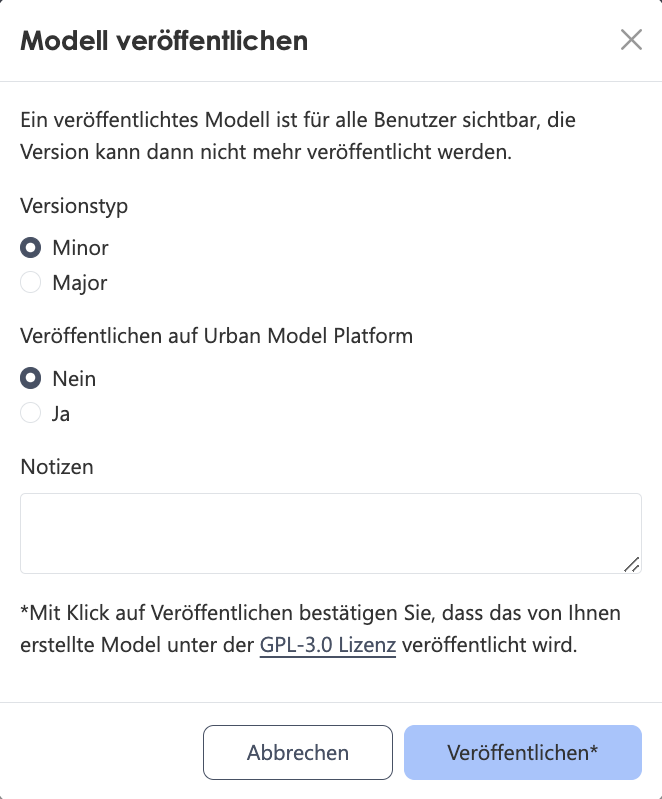 | Publish Model |
|
 | Activebar |
|
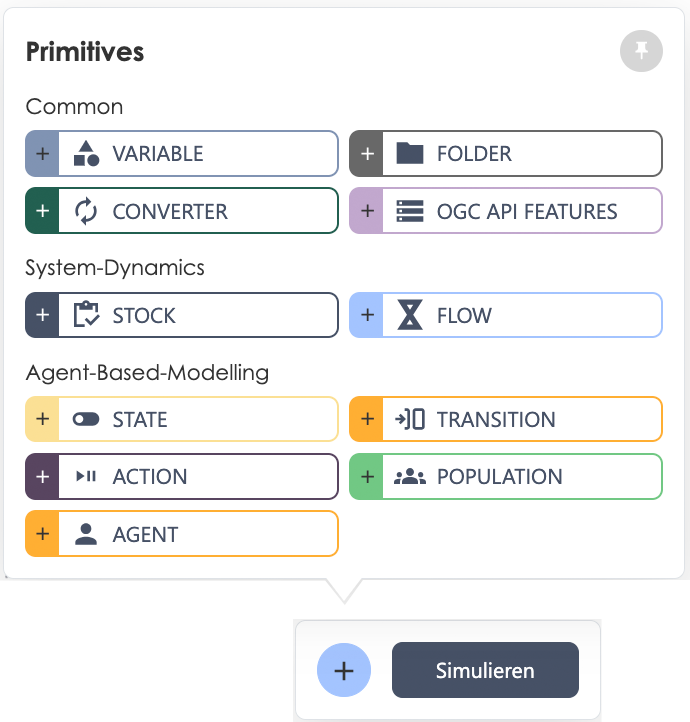 | Primitives |
|
 | Simulation Results |
|
 | Canvas |
|
 | Primitive Settings Window |
|
  | Scenario Settings |
|
Here you’ll find some important definitions at a glance!
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Model | A simplified, abstract representation of a real or imagined system that approximates certain aspects of the system depending on its purpose. Models can be physical, conceptual, or mathematical. |
| Model Structure | The formal organization of a model, consisting of equations, dependencies (SD) or states, rules, and interactions (ABM). Defines the functional logic of the system. |
| System Dynamics | A model-based approach to studying and describing complex, feedback-driven systems using stock and flow variables. Particularly suited for aggregated, long-term developments. |
| Agent-Based Modeling | Simulates systems through the interaction of many individual, autonomous agents, each following its own rules and goals. Suitable when individual behavior and interactions are key to system dynamics. |
| Causal Diagram | A visualization of cause–effect relationships, often used as a precursor or documentation for SD models. Shows qualitative system connections. |
| System Boundary | Defines the limits of the modeled system relative to its environment, determining which variables are included or excluded. |
| Simulation | Examining a system over time to analyze the behavior of a real or digital model under specific conditions. |
| Initialization | Defining the initial conditions of a model (e.g., start values, configurations). Essential for reproducibility and comparability. |
| Discretization | Converting continuous processes into discrete time steps (especially in SD models), affecting numerical accuracy and runtime. |
| Agent Interaction | In ABM: explicit coupling of agents via spatial proximity, rules, networks, or messaging. Leads to emergent behavior. |
| Rule-Based Modeling | Modeling approach where decisions or state transitions follow explicit rules. Common in ABM, especially for state transitions. |
| Dynamic Feedback | Circular causal relationships that evolve over time. In SD: positive feedback leads to growth, negative to stabilization. |
| Scenario Management | Methodical definition, execution, and evaluation of various future developments. In SD: via parameter combinations; in ABM: also via alternative rule sets. |
| Robust Decision Support | Identifying strategies that remain effective under high uncertainty and many possible futures (e.g., Robust Decision Making). |
| Calibration | Adjusting model parameters to empirical data to optimize the match to observed reality. |
| Verification | Technical check to ensure the model is implemented correctly — “Are we building the model right?” e.g., debugging, unit testing, source code review. |
| Validation | Assessing whether the model is consistent with the real system — “Are we building the right model?” e.g., expert feedback, data comparison, retrodiction. |
| Hybrid Modeling | Combining different modeling paradigms (e.g., SD+ABM) to capture both individual and systemic dynamics. |
| API (Application Programming Interface) | A standardized interface for software components to communicate. Defines how functions, data, or services are accessed and used by other applications without exposing internal structures. |
| Model Evaluation | Holistic assessment of a model in terms of assumptions, logic, results, plausibility, transparency, and applicability. |
| Behavioral Assumptions | Theoretically or empirically derived hypotheses about how actors make decisions or change states. Critical in ABM. |
| Versioning | Traceable storage of model development stages (e.g., via Git). Essential for reproducibility and collaboration. |
| Model Transparency | The degree to which a model, its structure, and assumptions are openly documented and made understandable — a foundation for trust and reuse. |